Linux chmod命令
Linux chmod(英文全拼:change mode)命令是控制用户对文件的权限的命令
Linux/Unix 的文件调用权限分为三级 : 文件所有者(Owner)、用户组(Group)、其它用户(Other Users)。
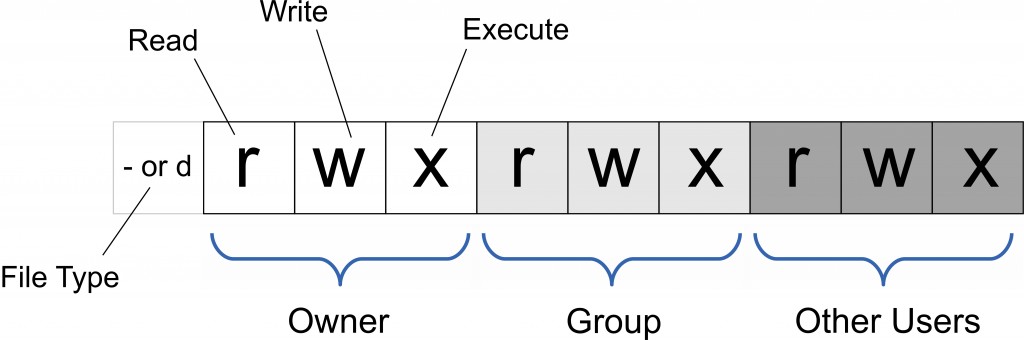
只有文件所有者和超级用户可以修改文件或目录的权限。可以使用绝对模式(八进制数字模式),符号模式指定文件的权限。
使用权限 : 所有使用者
语法
chmod [-cfvR] [--help] [--version] mode file...
参数说明
mode : 权限设定字串,格式如下 :
[ugoa...][[+-=][rwxX]...][,...]
其中:
- u 表示该文件的拥有者,g 表示与该文件的拥有者属于同一个群体(group)者,o 表示其他以外的人,a 表示这三者皆是。
- + 表示增加权限、- 表示取消权限、= 表示唯一设定权限。
- r 表示可读取,w 表示可写入,x 表示可执行,X 表示只有当该文件是个子目录或者该文件已经被设定过为可执行。
其他参数说明:
- -c : 若该文件权限确实已经更改,才显示其更改动作
- -f : 若该文件权限无法被更改也不要显示错误讯息
- -v : 显示权限变更的详细资料
- -R : 对目前目录下的所有文件与子目录进行相同的权限变更(即以递归的方式逐个变更)
- –help : 显示辅助说明
- –version : 显示版本
符号模式
使用符号模式可以设置多个项目:who(用户类型),operator(操作符)和 permission(权限),每个项目的设置可以用逗号隔开。 命令 chmod 将修改 who 指定的用户类型对文件的访问权限,用户类型由一个或者多个字母在 who 的位置来说明,如 who 的符号模式表所示:
| who | 用户类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| u | user | 文件所有者 |
| g | group | 文件所有者所在组 |
| o | others | 所有其他用户 |
| a | all | 所用用户, 相当于 ugo |
operator 的符号模式表:
| Operator | 说明 |
|---|---|
| + | 为指定的用户类型增加权限 |
| - | 去除指定用户类型的权限 |
| = | 设置指定用户权限的设置,即将用户类型的所有权限重新设置 |
permission 的符号模式表:
| 模式 | 名字 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| r | 读 | 设置为可读权限 |
| w | 写 | 设置为可写权限 |
| x | 执行权限 | 设置为可执行权限 |
| X | 特殊执行权限 | 只有当文件为目录文件,或者其他类型的用户有可执行权限时,才将文件权限设置可执行 |
| s | setuid/gid | 当文件被执行时,根据who参数指定的用户类型设置文件的setuid或者setgid权限 |
| t | 粘贴位 | 设置粘贴位,只有超级用户可以设置该位,只有文件所有者u可以使用该位 |
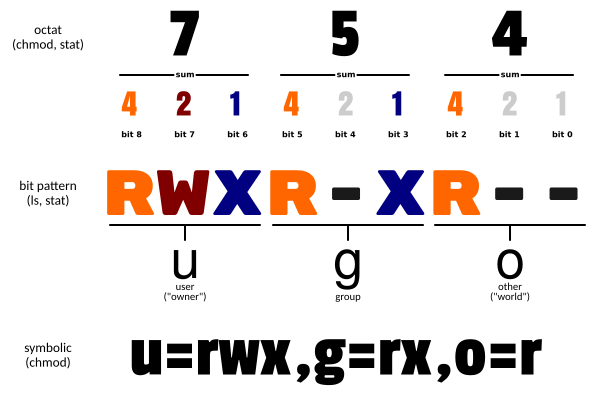
八进制语法
chmod命令可以使用八进制数来指定权限。文件或目录的权限位是由9个权限位来控制,每三位为一组,它们分别是文件所有者(User)的读、写、执行,用户组(Group)的读、写、执行以及其它用户(Other)的读、写、执行。历史上,文件权限被放在一个比特掩码中,掩码中指定的比特位设为1,用来说明一个类具有相应的优先级。
| # | 权限 | rwx | 二进制 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 读 + 写 + 执行 | rwx | 111 |
| 6 | 读 + 写 | rw- | 110 |
| 5 | 读 + 执行 | r-x | 101 |
| 4 | 只读 | r– | 100 |
| 3 | 写 + 执行 | -wx | 011 |
| 2 | 只写 | -w- | 010 |
| 1 | 只执行 | –x | 001 |
| 0 | 无 | — | 000 |
例如, 765 将这样解释:
- 所有者的权限用数字表达:属主的那三个权限位的数字加起来的总和。如 rwx ,也就是 4+2+1 ,应该是 7。
- 用户组的权限用数字表达:属组的那个权限位数字的相加的总和。如 rw- ,也就是 4+2+0 ,应该是 6。
- 其它用户的权限数字表达:其它用户权限位的数字相加的总和。如 r-x ,也就是 4+0+1 ,应该是 5。
实例
将文件 file1.txt 设为所有人皆可读取 :
chmod ugo+r file1.txt
将文件 file1.txt 设为所有人皆可读取 :
chmod a+r file1.txt
将文件 file1.txt 与 file2.txt 设为该文件拥有者,与其所属同一个群体者可写入,但其他以外的人则不可写入 :
chmod ug+w,o-w file1.txt file2.txt
为 ex1.py 文件拥有者增加可执行权限:
chmod u+x ex1.py
将目前目录下的所有文件与子目录皆设为任何人可读取 :
chmod -R a+r *
此外chmod也可以用数字来表示权限如 :
chmod 777 file
语法为:
chmod abc file
其中a,b,c各为一个数字,分别表示User、Group、及Other的权限。
r=4,w=2,x=1
- 若要 rwx 属性则 4+2+1=7;
- 若要 rw- 属性则 4+2=6;
- 若要 r-x 属性则 4+1=5。
chmod a=rwx file
和
chmod 777 file
效果相同
chmod ug=rwx,o=x file
和
chmod 771 file
效果相同
若用 chmod 4755 filename 可使此程序具有 root 的权限。
更多说明
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| chmod a+r file | 给file的所有用户增加读权限 |
| chmod a-x file | 删除file的所有用户的执行权限 |
| chmod a+rw file | 给file的所有用户增加读写权限 |
| chmod +rwx file | 给file的所有用户增加读写执行权限 |
| chmod u=rw,go= file | 对file的所有者设置读写权限,清空该用户组和其他用户对file的所有权限(空格代表无权限) |
| chmod -R u+r,go-r docs | 对目录docs和其子目录层次结构中的所有文件给用户增加读权限,而对用户组和其他用户删除读权限 |
| chmod 664 file | 对file的所有者和用户组设置读写权限, 为其其他用户设置读权限 |
| chmod 0755 file | 相当于u=rwx (4+2+1),go=rx (4+1 & 4+1)。0 没有特殊模式。 |
| chmod 4755 file | 4设置了设置用户ID位,剩下的相当于 u=rwx (4+2+1),go=rx (4+1 & 4+1)。 |
| find path/ -type d -exec chmod a-x {} \; | 删除可执行权限对path/以及其所有的目录(不包括文件)的所有用户,使用’-type f’匹配文件 |
| find path/ -type d -exec chmod a+x {} \; | 允许所有用户浏览或通过目录path/ |
1.1.常见权限说明
目录默认权限:755,文件默认权限:644
- 目录:
755750700 - 文件:
644640600
2.系统帮助
- 用法:chmod [选项]… 模式[,模式]… 文件…
- 或:chmod [选项]… 八进制模式 文件…
- 或:chmod [选项]… —reference=参考文件 文件…
- Change the mode of each FILE to MODE.
- With —reference, change the mode of each FILE to that of RFILE.
- –c, —changes like verbose but report only when a change is made
- –f, —silent, —quiet suppress most error messages
- –v, —verbose output a diagnostic for every file processed
- —no–preserve–root do not treat ‘/’ specially (the default)
- —preserve–root fail to operate recursively on ‘/’
- —reference=RFILE use RFILE‘s mode instead of MODE values
- -R, –recursive 权限递归
- –help 显示此帮助信息并退出
- –version 显示版本信息并退出
- Each MODE is of the form ‘[ugoa]*([-+=]([rwxXst]*|[ugo]))+|[-+=][0–7]+‘.
- GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
- 请向<http://translationproject.org/team/zh_CN.html> 报告chmod 的翻译错误
- 要获取完整文档,请运行:info coreutils ‘chmod invocation‘
3.图解
| 文件下载 | 文件名称:文件权限图.vsdx | 文件大小:34.7kb |
| 下载声明:本站文件大多来自于网络,仅供学习和研究使用,不得用于商业用途,如有版权问题,请联系我! | ||
| 下载地址:点击下载 | ||
提取密码:
4.示例
4.1.移除用户写权限
- [root@itbkz s]#mkdir mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#touch mulu/test.txt
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxr–xr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll mulu/test.txt
- –rw–r—r— 1 root root 0 12月 5 17:00 mulu/test.txt
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod u=rx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xr–xr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod u-w mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xr–xr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法3:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 555 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xr–xr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.2.增加属组写权限
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod g+w mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxrwxr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod g=rwx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxrwxr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法3:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 775 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxrwxr–x 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.3.增加其它写权限
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod o+w mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxr–xrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod o=rwx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxr–xrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法3:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 757 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxr–xrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.4.相同权限修改
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod go=rwx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 777 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.5.不同权限修改
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod u=rx,g=rwx,o=rwx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xrwxrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod u=rx,go=rwx mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xrwxrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法3:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 577 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- dr–xrwxrwx 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.6.删除全部权限
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod a= mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- d——— 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 000 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- d——— 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
- 方法3:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod =0 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu
- d——— 2 root root 22 12月 5 17:00 mulu
4.7.权限递归
- 方法1:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod -R 700 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu mulu/test.txt
- drwx—— 2 root root 22 12月 6 22:21 mulu
- –rwx—— 1 root root 0 12月 6 22:21 mulu/test.txt
- 方法2:
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod -R u=rwx,go= mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll -d mulu mulu/test.txt
- drwx—— 2 root root 22 12月 6 22:24 mulu
- –rwx—— 1 root root 0 12月 6 22:24 mulu/test.txt
5.注意
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 7777 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll
- 总用量 0
- drwsrwsrwt 2 root root 6 12月 5 23:34 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#chmod 7666 mulu
- [root@itbkz s]#ll
- 总用量 0
- drwSrwSrwT 2 root root 6 12月 5 23:34 mulu
 Linux 命令大全
Linux 命令大全