升级到Debian9后,我们发现系统默认不带/etc/rc.local文件,但rc.local服务仍然保留
补齐缺失文件,让Debian9通过编辑/etc/rc.loacl文件为我们的服务添加开机自启动
1、添加rc-local.service
#以下为一整条命令,一起复制运行cat > /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service <
[Unit]
Description=/etc/rc.local
ConditionPathExists=/etc/rc.local
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start
TimeoutSec=0StandardOutput=tty
RemainAfterExit=yes
SysVStartPriority=99
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
2、新建rc-local文件
#以下为一整条命令,一起复制运行cat > /etc/rc.local <
#!/bin/sh -e
#
# rc.local#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will “exit 0” on success or any other# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution# bits.#
# By default this script does nothing.
#
exit 0
EOF
3、添加权限并设置开机自启chmod +x /etc/rc.local
systemctl enable rc-local
systemctl start rc-local.service
检查状态:systemctl status rc-local.service
返回Active:active信息,则成功。
最后我们就可以在/etc/rc.local里,添加开机的自启命令什么的了。记住添加在exit 0之前。
注意:更改自启脚本后,需要重新运行一下命令已使其生效。systemctl enable rc-local
systemctl start rc-local.service
Debian添加开机启动项
例如:将test.sh脚本添加到开机自启。
1.将 test.sh 脚本放到 /etc/init.d/ 目录下
cp test.sh /etc/init.d/
cd /etc/init.d/
chmod +x test.sh
2.设置开机自启
update-rc.d test.sh defaults
运行 update-rc.d 很可能会出现错误提示:
insserv: warning: script 'test.sh' missing LSB tags and overrides
这是因为 test.sh 不符合 debian 开机自启文件的内容规范,debian 要求文件头部有启动信息。参考同目录下的 /etc/init.d/skeleton 文件头,把以下内容复制到 test.sh 再运行 update-rc.d test.sh defaults 。
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: test
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs
# Should-Start: $network
# Should-Stop: $network
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: test
# Description: test
### END INIT INFO
启动
update-rc.d -f test.sh remove方法二
执行脚本:
#!/bin/bash
# 删除可能已存在的 MyStartup
FileName=”MyStartup”
rm /etc/init.d/$FileName
rm /etc/rc3.d/S01$FileName
rm /etc/rc4.d/S01$FileName
rm /etc/rc5.d/S01$FileName
# 向 MyStartup 中写入需要执行的命令
echo “#!/bin/bash” > /etc/init.d/$FileName
echo “ls /root/ > /root/doc.txt” >> /etc/init.d/$FileName
chmod +x /etc/init.d/$FileName
ln -s /etc/init.d/$FileName /etc/rc3.d/S01$FileName
ln -s /etc/init.d/$FileName /etc/rc4.d/S01$FileName
ln -s /etc/init.d/$FileName /etc/rc5.d/S01$FileName
————————————————
在/etc/init.d/ 下新建启动脚本,在 /etc/rc2.d/ 下用软链接,链接此脚本即可。
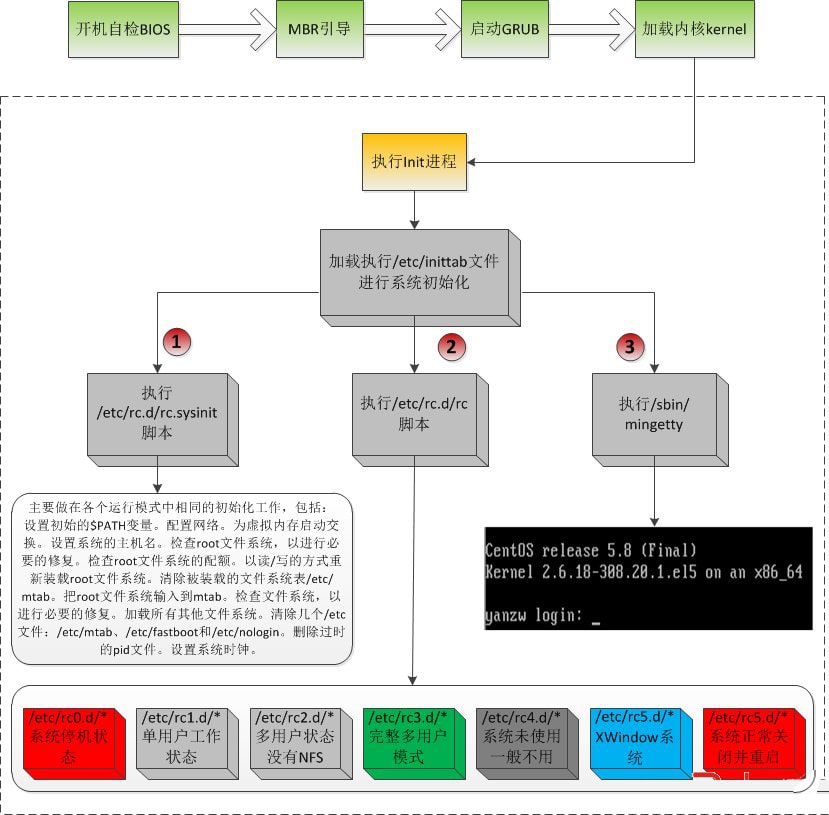
1. /etc下rc?.d 目录简介
/etc 下有 rc0.d — rc6.d
分别代表不同的级别:
0: 关闭计算机
1: 单用户模式
2: 无网络多用户模式
3: 有网络多用户模式
4: 保留作自定义,否则同运行级 3
5: 同运行级 4,一般用于图形界面(GUI)登录(如 X的 xdm 或 KDE的 kdm)
6: 重启动计算机
在 /etc/rc?.d 每个目录下都包含许多符号链接,其中一些以 K 字母开头,另外一些以 S 字母开头, 这些链接名在首字母后面都跟着两个数字。 这个 K 的含义是停止 (kill) 一个服务, S 的含义是启动一个服务。而数字则确定这些脚本的启动顺序,从 00 到 99(数字越小执行的越早)。 当 init 转换到其它运行级时, 一些相应的服务会停止, 而另一些服务则会启动。
真正的脚本在 /etc/init.d 目录下, 它们完成实际工作, 符号链接都是指向它们的。 停止脚本的链接和启动脚本的链接都指向 /etc/init.d 目录下的同一个脚本。 这是因为调用这些脚本时可以使用不同的参数,例如 start, stop, restart, reload, 和 status。 当调用 K 链接时,相应的脚本用 stop参数运行;当调用 S 链接时,相应的脚本用start 参数运行。
上面的说明有一个例外,在 rc0.d 和 rc6.d 目录下以 S 开头的链接不会启动任何东西, 而是用stop参数调用, 来停止某些服务。 这背后的逻辑是, 当用户要重启或关闭系统的时候, 不会要启动什么服务, 只会要系统停止。
以下是脚本参数的描述:
start
- 启动服务。
stop
- 停止服务。
restart
- 关闭服务,然后再启动。
reload
- 该服务的配置已更新。如果修改了某个服务的配置文件,又不必重启这个服务的时候, 可以使用这个参数
status
- 显示服务的状态,如果服务正在运行,会显示该服务进程的 PID 。
您可以自由修改启动进程工作的方式。 我们这里给出的文件只是它们怎样工作的一个示例而已。
2. 编写简单的启动脚本
# vi /etc/init.d/bin.sh
- #!/bin/sh
- #chkconfig:2345 80 05 –指定在哪几个级别执行,0一般指关机,6指的是重启,其他为正常启动。80为启动的优先级,05为关闭的优先级别
- #description:simple example service
- RETVAL=0
- start(){ #启动服务的入口函数
- echo “simple example service is started…”
- }
- stop(){ #关闭服务的入口函数
- echo “simple example service is stoped…”
- }
- #使用case选择
- case $1 in
- start)
- start #调用上面的start函数
- ;;
- stop)
- stop #调用上面的stop函数
- ;;
- *)
- echo “error choice ! please input start or stop”;;
- esac
- exit $RETVA # chmod +x /etc/init.d/bin.sh //加可执行权限
# /etc/init.d/bin.sh start //测试
3. 将启动脚本链接到 /etc/rc2.d
# ln -s /etc/init.d/bin.sh /etc/rc2.d/S20bin //作用:开机启动时会执行 /etc/init.d/bin.sh start
# ln -s /etc/init.d/bin.sh /etc/rc0.d/K20bin //作用: 关闭计算机时执行 /etc/init.d/bin.sh stop
4. 重启(此方法一直未能通过,希望大家可以提出一些建议,灰常感谢!)



